

What is a Threadlocker and when to use one?
Posted on 05/13/21 in: Technical Knowledge | | Agriculture | Horizontal Directional Drilling | Oilfield | Utilities / Power Generation | Valve Maintenance | Water Well | Oil & Gas | Mining | General Industry | Manufacturing | Author: Don Howard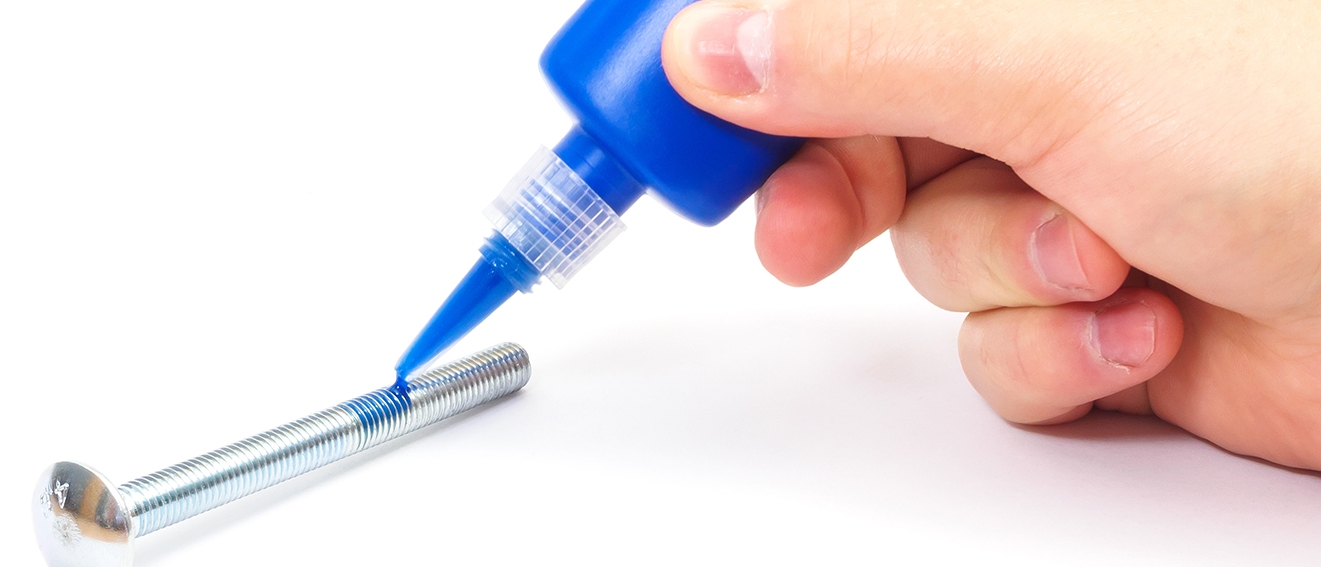
A threadlocker is a hard-setting sealant and adhesive compound used to lock threaded connections. Between all industries, home and DIYers, there are millions of threaded connections made each year and every one of them tends to loosen with time unless they are mechanically or chemically locked. The main causes of loosening, that is the loss of clamp force, are load, vibration and corrosion. Threadlockers are used in many cases in place of traditional mechanical washers and fasteners and often outperform the mechanical solutions.
Most threadlockers are anaerobic epoxies that create a strong bond between opposing threads and fill surface imperfections, locking the threads in place. “Anaerobic” refers to the property of an epoxy curing in the absence of oxygen which is not present in the sealed threads. There are different kinds of threadlockers ranging from general-purpose to those for use in specific applications or environments.
A good threadlocker should cover the following properties:
- Vibration resistance
- Anticipated load resistance
- An acceptable cure time at room temperature
- Chemical compatibility with acids, alkalis, water, hydrocarbons and solvents, as required
- Corrosion resistance
- An acceptable consistency for easy, even application
What are the common applications of a Threadlocker?
Threadlockers are used in different applications, from Residential, MRO Industrial to specific Industrial Equipment. Some of these applications include:
- Horizontal Directional Drilling
- Oil & Gas Drilling
- Water Pipeline Assemblies
- Gas Line Assemblies
- Automotive Maintenance
- Aerospace Assemblies
- MRO Industrial

When to use a Threadlocker?
The use of a threadlocker is recommended when a threaded faster will be subjected to vibration and/or dynamic load. Even if these conditions are not factors, thread lockers are recommended when threaded assemblies may jeopardize joint quality and function causing wear, fretting wear, fretting corrosion, joint failure, etc.
How strong is a 2-Part Epoxy Adhesive?
Tensile strength varies by type and grade but is often over 28N/mm² (4000psi). Some great advantages of using 2-part epoxies are that they adhere strongly to many substrates, cure times are reasonable and they cure at ambient temperature.
Using a two-part epoxy threadlocker in joints that are constantly exposed to stresses like vibration, dynamic and shock loads, thermal expansion and contraction, etc., can dramatically reduce joint failure and downtime and the maintenance and production costs associated with it.

How to apply a Threadlocker
Typically, threadlockers are simple to apply in just 4 steps.
Step 1: Make sure the surfaces are clean, dry and totally free of grease, oil and rust preventive.
Step 2: Select the right threadlocker to be used on the application. With 2-part epoxy thread lockers, the resin and activator or hardener need to be mixed in a specific ratio to get the best result.
Step 3: Apply the compound evenly on one of the threaded contact surfaces. The threadlocker is really only needed where the threads will be joined.
Step 4: Assemble the fastener per the recommended torque or clamp force and let the threadlocker cure at room temperature. Follow the manufacturer's guide to know the curing time.
